Protect your data and applications no matter where they reside to avoid costly business interruptions or to meet compliance requirements. Securely extend your on-premises backup storage and data archiving solutions to the cloud—reducing cost and complexity, while achieving efficiency and scalability.
The Azure Backup service provides simple, secure, and cost-effective solutions to back up your data and recover it from the Microsoft Azure cloud.
Azure storage offers different access tiers, which allow you to store blob object data in the most cost-effective manner. One of the access tier is Archive tier.
The archive access tier has the lowest storage cost. But it has higher data retrieval costs compared to the hot and cool tiers. Data in the archive tier can take several hours to retrieve. Data must remain in the archive tier for at least 180 days or be subject to an early deletion charge.
While a blob is in archive storage, the blob data is offline and can’t be read, copied, overwritten, or modified. You can’t take snapshots of a blob in archive storage. However, the blob metadata remains online and available, allowing you to list the blob and its properties
What can I back up?
- On-premises – Back up files, folders, system state using the Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) agent. Or use the DPM or Azure Backup Server (MABS) agent to protect on-premises VMs (Hyper-V and VMWare) and other on-premises workloads.
- Azure VMs – Back up entire Windows/Linux VMs (using backup extensions) or back up files, folders, and system state using the MARS agent.
- Azure Files shares – Backup and restore Azure File shares to storage account.
- SQL Server in Azure VMs – Back up SQL Server databases running on Azure VMs.
- SAP HANA databases in Azure VMs – Backup SAP HANA databases running on Azure VMs.
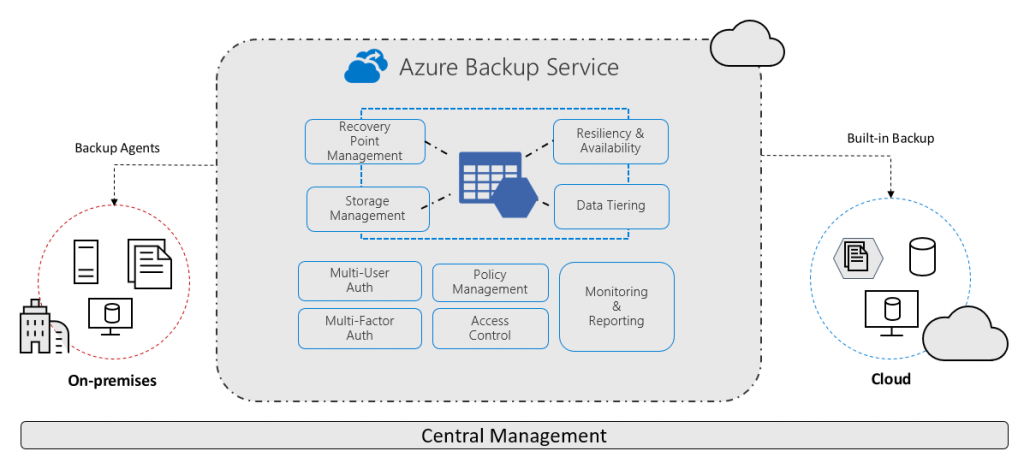
Why use Azure Backup?
Azure Backup delivers these key benefits:
- Offload on-premises backup: Azure Backup offers a simple solution for backing up your on-premises resources to the cloud. Get short and long-term backup without the need to deploy complex on-premises backup solutions.
- Back up Azure IaaS VMs: Azure Backup provides independent and isolated backups to guard against accidental destruction of original data. Backups are stored in a Recovery Services vault with built-in management of recovery points. Configuration and scalability are simple, backups are optimized, and you can easily restore as needed.
- Scale easily – Azure Backup uses the underlying power and unlimited scale of the Azure cloud to deliver high-availability with no maintenance or monitoring overhead.
- Get unlimited data transfer: Azure Backup doesn’t limit the amount of inbound or outbound data you transfer, or charge for the data that is transferred.
- Keep data secure: Azure Backup provides solutions for securing data in transit and at rest.
- Centralized monitoring and management: Azure Backup provides built-in monitoring and alerting capabilities in a Recovery Services vault. These capabilities are available without any additional management infrastructure. You can also increase the scale of your monitoring and reporting by using Azure Monitor.
- Get app-consistent backups: An application-consistent backup means a recovery point has all required data to restore the backup copy. Azure Backup provides application-consistent backups, which ensure additional fixes aren’t required to restore the data. Restoring application-consistent data reduces the restoration time, allowing you to quickly return to a running state.
- Retain short and long-term data: You can use Recovery Services vaults for short-term and long-term data retention.
- Automatic storage management – Hybrid environments often require heterogeneous storage – some on-premises and some in the cloud. With Azure Backup, there’s no cost for using on-premises storage devices. Azure Backup automatically allocates and manages backup storage, and it uses a pay-as-you-use model. So you only pay for the storage you consume.
- Multiple storage options – Azure Backup offers two types of replication to keep your storage/data highly available.
- Locally redundant storage (LRS): replicates your data three times (it creates three copies of your data) in a storage scale unit in a datacenter. All copies of the data exist within the same region. LRS is a low-cost option for protecting your data from local hardware failures.
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS): is the default and recommended replication option. GRS replicates your data to a secondary region (hundreds of miles away from the primary location of the source data). GRS costs more than LRS, but GRS provides a higher level of durability for your data, even if there’s a regional outage.

